Communication Network and Infrastructure
Background
XAG is dedicated to bringing drones, robots, autopilot, artificial intelligence, and Internet-of- things into the world of agricultural production. During the development, the XAG UAV experiences a significant change on the communication Mechanisms.
XAG products roadmap
|
Year |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
|
Model |
XP2020 |
P40, V40 |
P100 |
Communication Mechanisms Comparison
|
XP2020 |
P40, V40, P100 |
|||
|
Communication Mechanisms |
Local computing + mesh network + 4G |
Cloud Computing in IoT using 4G |
Duo Channel (4G/WIFI) |
Local Network Terminal |
|
Does it need 4G? |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Does it use WIFI? |
Yes, mesh network |
No |
Yes |
Yes, LNT work as a WIFI hub. |
|
Remote Controller |
ACS2 2020 |
ACS2 2021 |
ACS2 2021 |
ACS2 2021 |
|
Android APP |
XAG Agri 2 |
XAG One |
XAG One |
XAG One |
|
RTK station |
Portable station (WIFI) |
Fix Station (4G) |
Fix Station (4G) |
Portable Station (WIFI) |
Overview
For XAG agriculture UAV (model 2021 above), the essential components of UAV-based network and infrastructures are UAV, ACS2 2021, XRTK4 portable station and XAG One App running on smartphone. Respected to different environment, there are three networking mode.
|
No. |
Networking mode |
Under Environment |
|
1 |
Cloud Computing in IoT (4G) |
Good 4G Network |
|
2 |
Duo Channel (4G/WIFI) |
Poor 4G Network |
|
3 |
Local Network Terminal |
No 4G Network |
Network Devices
|
ACS2 Remote controller |
||
|
Model |
Description |
Photo |
|
ACS2 2020 |
Used on XP2020 with XRTK4 portable station, fixed station, and CORS Identical hardware as ACS2 2021 But with ACS2 2020 firmware installed |
|
|
ACS2 2021 |
Used on V40/P40/P100 with XRTK portable, fixed station and CORS Identical hardware as ACS2 2020 but with ACS2 2021 firmware installed |
|

Indeed, you can literally update the ACS2 firmware from 2020 to 2021 as they have the identical hardware, but our backend server will not recognize this device as its serial number is not registered as ACS2 2021 device. Thus, it’s not allowed to add in your XAG One account.
|
RTK STATION |
||
|
MODEL |
Description |
Photo |
|
RTK FIX STATION |
Work as RTK base station, sending RTK/RTCM to cloud server through 4G network. |
|
|
RTK PORTABLE STATION |
As RTK base station, it’s optional to work with/without 4G network.
If it works in 4G network, insert the 4G into it and bring the RTK online. It will broadcast RTK/RTCM data through 4G. Add the RTK station in App device list.
If it works in WIFI, please add the RTK station in the LNT network. It will broadcast RTK/RTCM data through WIFI. |
|
Note: please be aware of that after the recent firmware update of RTK station, both portable and fix RTK station can broadcast RTCM/RTK through 4G network.
|
UAV Model |
||
|
Model |
Variant |
Photo |
|
P40
|
(CN) XAG P40 2021 STD UAV |
|
|
(EN) XAG P40 2021 STD UAV |
|
|
|
V40
|
(CN) XAG V40 2021 STD UAV |
|
|
(EN) XAG V40 2021 STD UAV |
|
|
|
P100
|
(CN) XAG P100 2021 STD UAV |
|
|
(EN) XAG P100 2021 STD UAV |
|
|
Networking Mode
4G Networking Mode
There are two variants of 4G networking mode. One is standard 4G networking mode, the other is Lite 4G networking mode. The difference between them is whether UAV has 4G SIM card inserted.
#1: Direct 4G Networking Mode: Cloud Computing in IoT
Introduction
When the 4G coverage and signal strength are good, all the devices can have the access to the XAG cloud server through 4G network. The advantage of using 4G networking mode is to eliminate the communication range. The disadvantage is that the UAV may be suffered from 4G network delay.
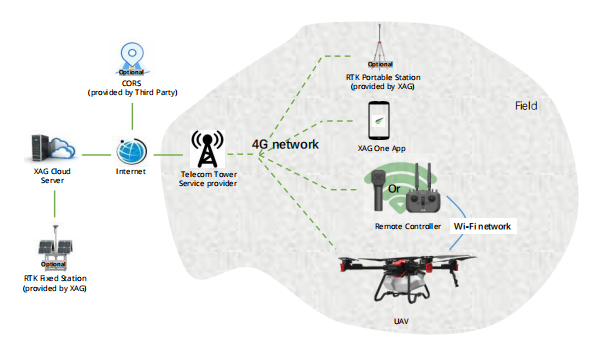
- Good 4G coverage in operation area
- Users have access to CORS or XAG Fixed station
Equipment Status on Wireless
|
Equipment |
4G Sim Card Inserted? |
Wi-Fi |
|
UAV |
Yes |
Connected to RC |
|
RC |
Yes |
AP (Access Point) |
|
XRTK4 (optional) |
Yes |
Disabled |
|
Smartphone/Pad |
Yes |
Disabled |
Requirements:
- Good4G network coverage
- If use GNSS/XRTK Fix station, the distance between operation and station must be within 30km because the common number of satellites should be above 16 and the weather condition can
- All the devices (XRTK Fixed Station/Smartphone/ACS2 2021/UAV) need to have 4GSIM card inserted. Depending on the use of UAV, the data plans can be varied. For reference:
|
Items (device) |
Data Plan |
|
GNSS/RTK Fix Station |
500M/month |
|
Smartphone (XAG One App) |
1G/month |
|
ACS2 2021 |
300M/month |
|
UAV |
1G/month |
#2: Semi-Direct 4G Networking Mode
Introduction
Our user is allowed to enable Wi-Fi communication channel between remote controller and UAV. In such way, the UAV is no longer required to insert 4G SIM card. However, it requires users manually pair the UAV to remote controller. This mode allows UAV to access internet through remote controller.
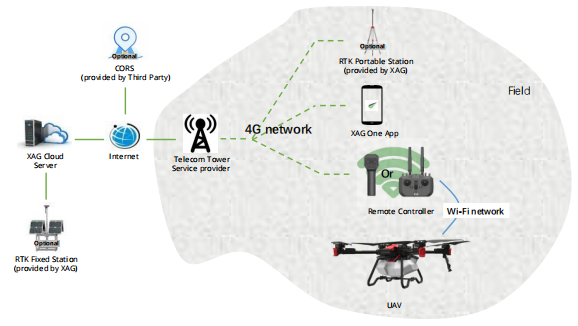
- Good 4G coverage in operation area
- Users have CORS account / XAG Fixed station.
Equipment Status on Wireless
|
Equipment |
4G Sim Card Inserted? |
Wi-Fi |
|
UAV |
No |
Connected to RC |
|
RC |
Yes |
AP (Access Point) |
|
XRTK4 |
Yes |
Disabled |
|
Smartphone |
Yes |
Disabled |
LNT Networking Mode
There are two variants of LNT networking mode. One is standard LNT networking mode, the other is Field mapping LNT Networking Mode. The difference between them is whether UAV has 4G SIM card inserted.
#1: Standard LNT Networking Mode
Local network terminal, abbr, LNT, is a type of networking mode that works without internet. It works as a local IOT server and communicate with other devices through the local Wi-Fi network. You can regard the LNT as the substitution of the cloud Server. LNT and its IOT devices must be properly upgraded and configured before use.
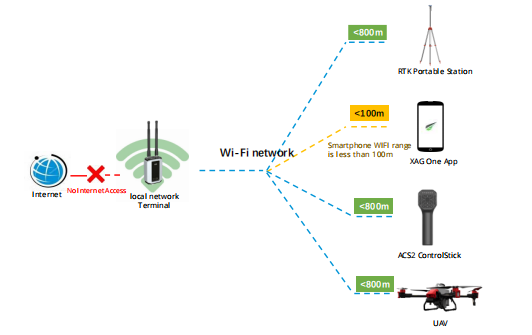
|
DESCRIPTION |
||
|
ITEMS (DEVICE) |
4G network |
WIFI (2.4/5.8GHz) |
|
GNSS/RTK PORTABLE STATION |
Not in use |
Sent RTK/RTCM reference to LNT; |
|
XAG ONE APP |
Not in use |
Communicate with LNT; UAV setting; Flight mission, UAV status, Field mapping, etc. firmware downloads and update, |
|
ACS2 2021 |
Not in use |
Communicate with LNT; Send manual control command to LNT |
|
UAV |
Not in use |
Communicate with LNT |
|
LNT |
N/A |
Local IOT server |
Requirements:
- GNSS/XRTK portable station is a must
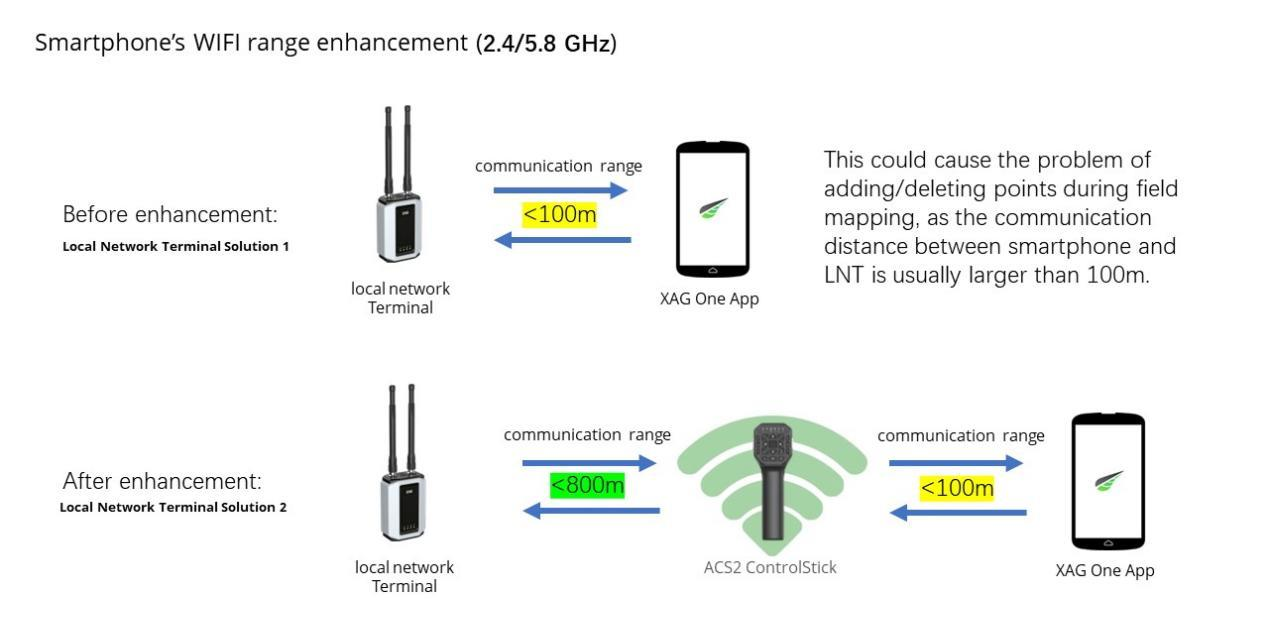
- LNT must be put in a high place, with battery supply. The LNT WIFI only allows the maximum communication range of 800m without any interference.
Awareness
- As the smartphone can only reach the LNT within 100m, if the ACS2 hotspot is unstable during field mapping, user can switch to the field mapping of LNT. Please read the next page.
Advantage:
- No 4G network is required. Thus, Smartphone, ACS2 2021 and UAV do not need 4G Due to the hardware safety check, XRTK portable station still need 4G Sim inserted but will use no data.
- No RTK fix station is required. Instead, the RTK portable station will be used. It means that the users no longer rely on the RTK fix station (only 30km) and can move around as they want.
Disadvantage:
- LNT has limited communication range, maximum 800m. Depending on various environments, this communication range can differ.
- Smartphone has limited communication. only the maximum range of 100mbetween smartphone and LNT
- LNT and its battery can be an extra cost.
#2: Field mapping LNT Networking Mode
This networking mode is only used in field mapping, please do not use it in flight mission. Otherwise, the UAV will suffer from huge network delay and keep switching between online and offline.
This mode is designed for field mapping. Some users may encounter huge network delay when using smartphone on field mapping as they usually walk into the field and stay far away from the LNT. As the smartphone only has the physical WIFI range less than 100 meters, the smartphone will disconnect from LNT if the smartphone stays too far from LNT. To solve the issue of short physical WIFI range between smartphone and LNT, we can connect our smartphone to ACS2 remote controller. From here, we can enhance the physical WIFI range of smartphone as ACS2 work as RP repeater.

The benefit of this solution is that the communication range between smartphone and LNT increase from 100m to 800m in ideal environment. It’s useful during field mapping, which the smartphone will be carried away from LNT.
Requirements:
- GNSS/XRTK portable station is a must.
- LNT must be put in a high place, with battery. The WIFI antenna of LNT only allows the maximum communication range of 800m.
- Connect smartphone to ACS2 2021 remote controller’s hotspot.
Advantage/disadvantage:
Same as local network terminal
|
DESCRIPTION |
||
|
ITEMS (DEVICE) |
4G network |
WIFI (2.4/5.8GHz) |
|
GNSS/RTK PORTABLE STATION |
Not in use |
Sent RTK/RTCM reference to LNT; |
|
XAG ONE, ANDROID APP |
Not in use |
Communicate with LNT through ACS2 2021 remote controller; UAV setting; Flight mission; Field mapping; firmware downloads and update |
|
ACS2 2021 |
Not in use |
Communicate with LNT; Send manual control command to LNT |
|
UAV |
Not in use |
Communicate with LNT |
|
LNT |
N/A |
Local IOT server |
Remote Controller Networking Mode (RCN)

There are four variants of RCN mode.
RCN Local
Semi-DirectRCN4G
Direct RCN4G
RCNWiFi
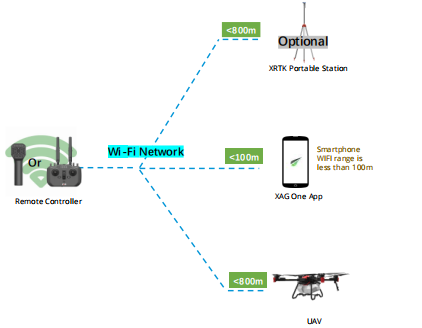
#1: RCN Local
Introduction
RC (Remote controller) networking mode is a type of networking mode that works without internet. It uses remote controller as the communication host in the local Wi-Fi network.
|
Local RCN |
||
|
|
4G SIM inserted? |
Wi-Fi |
|
UAV |
N |
Connect to RC |
|
RC |
N |
AP |
|
Smartphone/Pad |
N |
Connect to RC |
#2: Semi-Direct RCN4G (Standard)
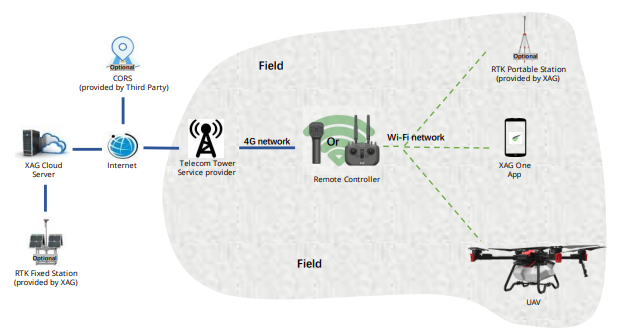
As local RCN mode is based on the local Wi-Fi network, which works perfectly fine when the field has no internet access. However, the internet inaccessibility will also affect the use of this UAV system. Basically, users may not be able to update the firmware online, or not able to use CORS, etc. Thus, semi-Direct RCN4G mode could solve these issues. Once a valid 4G SIM card is inserted into remote controller, the local RCN mode can automatically change to Semi-Direct RCN4G mode. Our UAV system will have communication to internet and allow users to use CORS or update firmware online.
|
Semi-Direct RCN4G |
||
|
|
4G SIM inserted? |
Wi-Fi |
|
UAV |
N |
Connect to RC |
|
RC |
Y |
AP |
|
Smartphone/Pad |
N/Y |
Connect to RC |
#3: Direct RCN4G
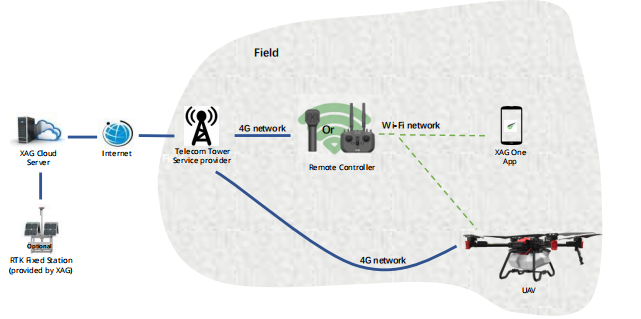
Semi RCN4G mode is good as our UAV system can have access to internet. But the remote controller works as AP and all other devices must go through it to access internet. However, the semi RCN4G may result in the high latency of CORS as the Wi-Fi network delay between UAV and RC happens in field operation. In this scenario, Direct RCN4G can solve this issue because the UAV can access internet directly without accessing RC Wi-Fi network. Once a valid 4G SIM card is inserted into remote controller, the Semi-Direct RCN mode can automatically change to Direct RCN4G mode.
|
Direct RCN4G |
||
|
|
4G SIM inserted? |
Wi-Fi |
|
UAV |
Y |
Connect to RC |
|
RC |
Y |
AP |
|
Smartphone/Pad |
N/Y |
Connect to RC |
RCN4G – CORS

RCN4G – RTK Portable Station

RCN4G – RTK Fixed Station
#4: RCNWiFi
RCNWiFi mode is very similar to Semi Direct RCN4G mode. In Semi Direct RCN4G, the remote controller connects to router. While in RCNWiFi, the remote controller connects to wireless access point (wired router or portable router). Field WiFi network may be provided by portable LTE router, wired router or mobile hotspot.
|
RCNWiFi |
||
|
|
4G SIM inserted? |
Wi-Fi |
|
UAV |
N |
Connect to RC |
|
RC |
N |
AP1: UAV/Phone; AP2: office/home router |
|
Smartphone/Pad |
N |
Connect to RC |
RCNWiFi - CORS
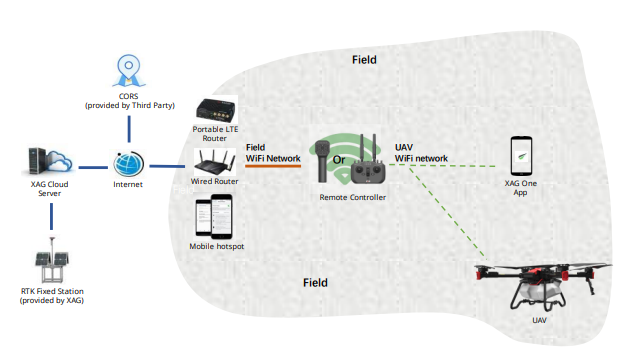
RCNWiFi - RTK portable station 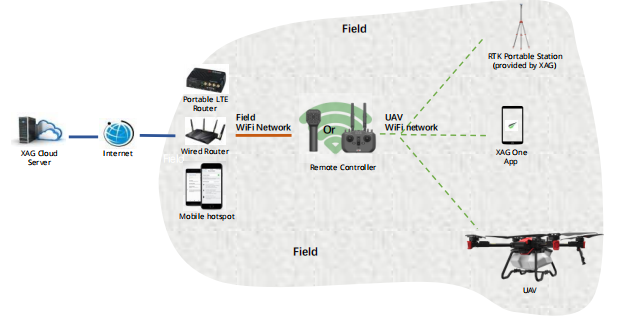
RCNWiFi – RTK fixed station
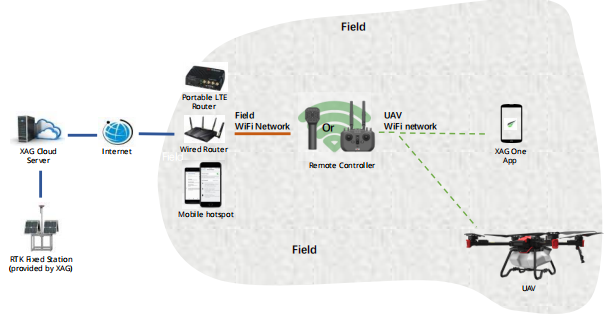
.png?height=120&name=Pegasus%20Robotics%20Logo%20-%20Portait%20(2).png)













